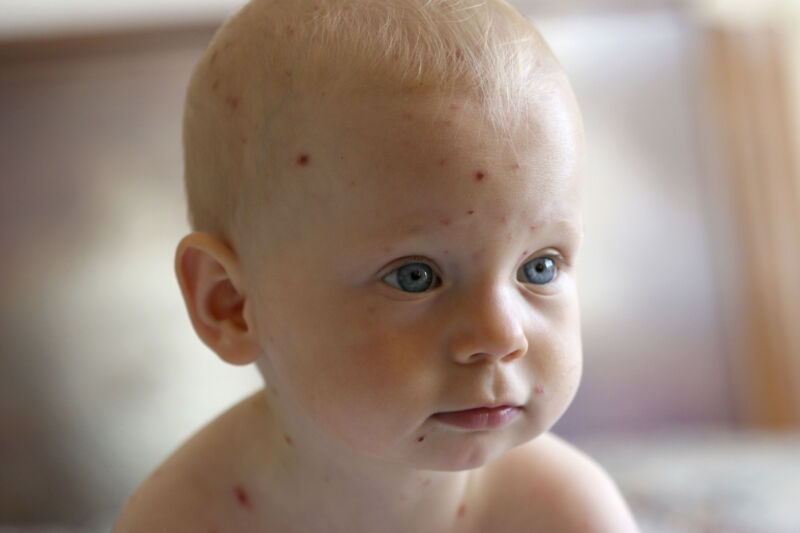
Thanks to the vaccination program that began in 1995, chickenpox is now relatively rare. Cases of the miserable, itchy condition have fallen more than 97 percent. But, while children have largely put the oatmeal baths and oven mitts behind them, doctors have apparently let their diagnostic skills get a little crusty.
According to a study published Thursday, public health researchers in Minnesota found that 55 percent of people diagnosed with chickenpox based on their symptoms were actually negative for the varicella-zoster virus, the virus that causes chickenpox. The study noted that the people were all diagnosed in person by health care providers in medical facilities. But, instead of chickenpox, lab testing showed that some of the patients were actually infected with an enterovirus, which can cause a rash, or the herpes simplex virus 1, which causes cold sores.
The study, published in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, supports expanding laboratory testing for suspected chickenpox cases in the state’s program and highlights that diagnoses based on symptoms are “unreliable.”
For one thing, doctors simply see far fewer chickenpox cases these days because of the protection from vaccines. While chickenpox cases in the US previously reached 4 million each year, with 10,500 to 13,500 hospitalizations and 100 to 150 deaths, there are now fewer than 150,000 cases,1,400 hospitalizations, and 30 deaths each year, the CDC reports. Vaccination is more than 90 percent effective at preventing the disease. In the rare cases where a vaccinated person contracts chickenpox, the muted rashes are challenging to identify by eye. But even in unvaccinated children, chickenpox can be tricky to pick out; it can easily be confused with measles, insect bites, enterovirus, skin infections such as scabies and impetigo, herpes viruses, and hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Since 2016, the Minnesota Department of Health has been working to expand laboratory testing, including outreach to health care providers and the public on the importance of testing to confirm suspected chickenpox cases.
Between 2016 and 2023, 208 people who were diagnosed with chickenpox in person at a medical facility submitted specimens for testing to the state health department. Only 93 of the 208 (45 percent) were positive for the virus. The vaccination status was known for 203 of the people—100 were vaccinated, 103 were not. Of the vaccinated people tested, only 22 (22 percent) turned out to have chickenpox, while 68 (66 percent) of the unvaccinated people had it, reflecting the efficacy of vaccination.
In a larger group of 420 people, which included people who were self-diagnosed, the accuracy rate was unsurprisingly lower. Of the 420 suspected chickenpox cases, only 157 (37 percent) were positive for the varicella-zoster virus. Of the remaining 263 people, 47 were positive for enterovirus, 20 were positive for herpes simplex virus 1, 0 were positive for herpes simplex virus 2 (genital herpes), two people had indeterminate test results, and 194 were negative for all four viruses tested.
The authors highlight that the findings are significant because people suspected of having chickenpox are recommended to stay home from school and work longer than people with other viral infections. More testing can ensure appropriate clinical management.

