
Microsoft is testing support for the Discovery of Network-designated Resolvers (DNR) internet standard, which enables automated client-side discovery of encrypted DNS servers on local area networks.
Without DNR support, users must manually enter the info of encrypted DNS servers on their local area network within the network settings.
However, client-side DNR automatically configures devices to reach such encrypted DNS resolvers and use encrypted DNS protocols like DNS over TLS (DoT), DNS over HTTPS (DoH), and DNS over QUIC (DoQ).
When a device with client-side DNR enabled joins a new network, it queries the local DHCP server, requesting an IP address and DNR-specific options.
The server, operating server-side DNR, responds with encrypted DNS details, including server IP, supported protocols, port numbers, and authentication data, allowing the client to establish an encrypted DNS tunnel automatically using the provided info.
“Until today, Windows Insiders users had to find out the IP address of their desired encrypted DNS server and manually enter it to configure client-side encrypted DNS on their machine,” said Microsoft’s Amanda Langowski and Brandon LeBlanc.
“DNR will enable Windows Insider users to use encrypted DNS protocols like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) on the client-side without requiring manual configuration.”
Support for client-side DNR is currently rolling out to Windows Insiders using Windows Insider build 25982 or above. This feature is not yet available on non-Insider Windows versions.
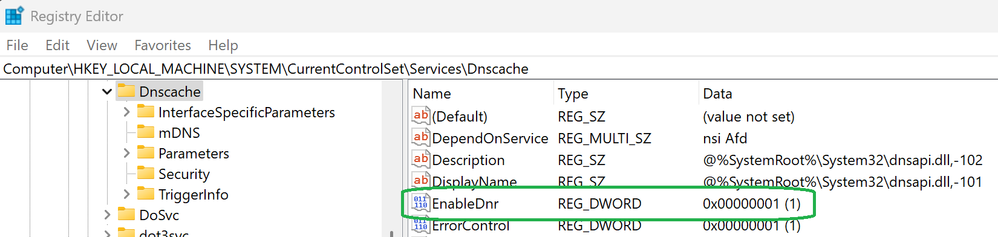
After installing a compatible Windows Insider build, you will have to create a new EnableDnr registry key under Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Dnscache to activate DNR on the device by running the following command from an elevated command prompt:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Dnscache\Parameters /v EnableDnr /t REG_DWORD /d 1
After the registry changes, you must restart the device so that the updated settings take effect. To see DNR in action, you must connect to a network where the DHCPv4 or DHCPv6 server has server-side DNR toggled on.
At the moment, Microsoft’s client-side DNR implementation only supports the following configuration modes (IPv6 RA Encrypted DNS is not yet supported):
To disable client-side DNR on your system, you can run the following command in an administrator command prompt and reboot the system for the change to take effect:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Dnscache\Parameters /v EnableDnr /t REG_DWORD /d 0
Starting with today’s Windows 11 Insider build, Microsoft also allows admins to require SMB client encryption for all outbound connections to defend against eavesdropping and interception attacks.
The company also added ReFS filesystem Block Cloning Support to the Windows copy engine to improve ReFS volumes’ performance when copying larger files.

