
Thierry Monasse/Getty Images
The Arctic Ocean is mostly enclosed by the coldest parts of the Northern Hemisphere’s continents, ringed in by Siberia, Alaska and the Canadian Arctic, with only a small opening to the Pacific through the Bering Strait, and some narrow channels through the labyrinth of Canada’s Arctic archipelago.
But east of Greenland, there’s a stretch of open water about 1,300 miles across where the Arctic can pour its icy heart out to the North Atlantic. Those flows include increasing surges of cold and fresh water from melted ice, and a new study in the journal Weather and Climate Dynamics shows how those pulses can set off a chain reaction from the ocean to the atmosphere that ends up causing summer heatwaves and droughts in Europe.
The large new inflows of fresh water from melting ice are a relatively new ingredient to the North Atlantic weather cauldron, and based on measurements from the new study, a currently emerging “freshwater anomaly” will likely trigger a drought and heatwave this summer in Southern Europe, said the study’s lead author, Marilena Oltmanns, an oceanographer with the United Kingdom’s National Oceanography Centre.
She said warmth over Greenland in the summer of 2023 melted a lot of ice, sending more freshwater toward the North Atlantic. Depending on the exact path of the influx, the findings suggest that, in addition to the immediate impacts this year, it will also trigger a heatwave and drought in Northern Europe in a more delayed reaction in the next five years, she said.
The coming extremes will probably be similar to the European heatwaves of 2018 and 2022, she added, when there were huge temperature spikes in the Scandinavian and Siberian Arctic, as well as unusual wildfires in far northern Sweden. That year, much of the Northern Hemisphere was scorched, with “22 percent of populated and agricultural areas simultaneously experiencing heat extremes between May and July,” according to a 2019 study in Nature.
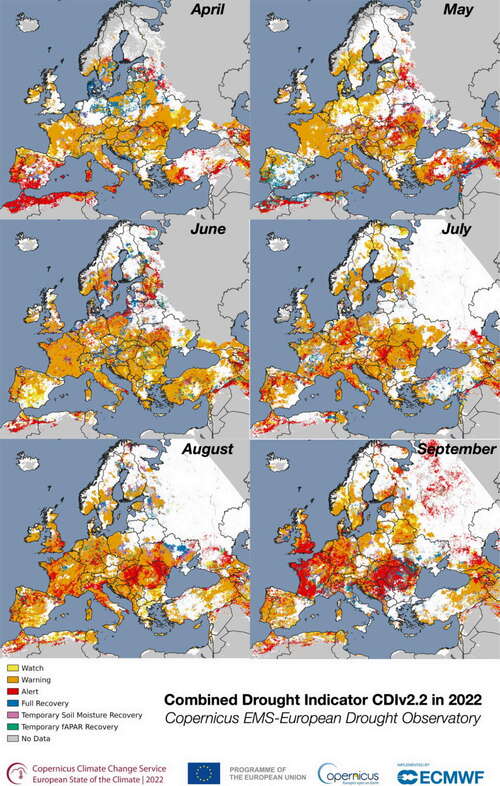
In 2022, persistent heat waves across Europe from May to August killed more than 60,000 people, subsequent research showed. The United Kingdom reported its first-ever 40° Celsius (104° Fahrenheit) reading that summer, and the European Union’s second-worst wildfire season on record burned about 3,500 square miles of land.
Meanwhile, 2022 was also Europe’s driest year on record, with 63 percent of its rivers showing below-average discharge and low flows hampering important river shipping channels as well as power production.
European Commission, Joint Research Centre
Oltmanns said the findings will help farmers, industries, and communities to plan ahead for specific weather conditions by developing more resilient agricultural methods, predicting fuel demand and preparing for wildfires.
Changing effects of freshwater flows into the North Atlantic had previously been observed over decadal timescales, associated with cyclical, linked shifts of ocean currents and winds, but that was “a very low frequency signal,” she said. “We have disentangled the signals.”
Now the fluctuations are more frequent and more intense, “switching between different states very rapidly,” she said, adding that the study shows how the ocean changes driven by freshwater inflows have “direct and immediate consequences on the atmospheric circulation,” and thus on subsequent weather patterns in Europe.

