Something to look forward to: PCs equipped with Nvidia RTX graphics cards have been capable of applying ML-based upscaling to video playback and streaming for almost a year – whether people actually use it is another question. Now, AMD is introducing similar technology to systems with a wider range of GPUs. It will be interesting to compare Team Red’s solution to the competition.
Among AMD’s CES 2024 announcements was the confirmation that the company will enable video enhancement through FSR upscaling. The functionality to upscale streaming videos will arrive with the next Radeon Adrenalin driver update, and an update to VLC supporting the technology for offline content will arrive sometime in the first quarter.
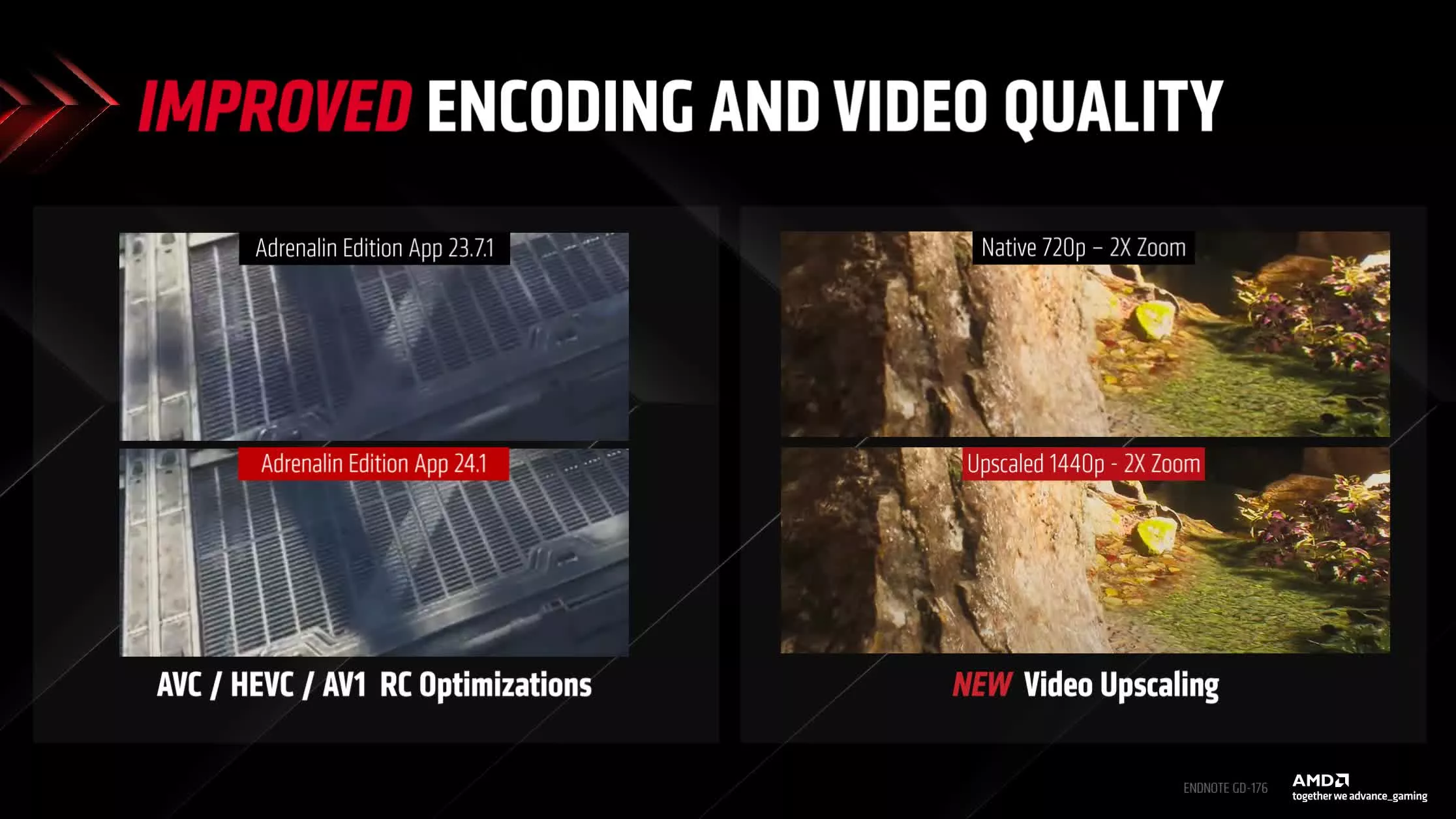
The reveal didn’t feature any live demonstrations, but AMD hinted that upscaling a YouTube video from 720p to 1440p could result in a noticeably clearer image.
Nvidia introduced RTX Video Super Resolution about a year ago, which offers upscaling support in the browser for YouTube and streaming services, as well as for offline footage in VLC. The initial reception of “RTX VSR” was quite modest, but it has received a more positive response from users following subsequent updates.
However, like DLSS, Nvidia’s solution only supports the company’s RTX graphics cards. Meanwhile, AMD FSR works on most hardware, including consoles and GPUs from competitors, so its video upscaling counterpart might be usable on a wide variety of devices. The company hasn’t listed system requirements or said whether it could bring video upscaling to non-PC systems.
It remains unclear which browsers will support this new functionality. RTX Video Super Resolution was not available on Firefox until well after its adoption by Chrome and Edge. Notably, Edge also includes a separate solution compatible with both Nvidia and AMD hardware, as does Opera GX. AMD’s FSR Video will inevitably be compared to Nvidia’s. In image quality comparisons, DLSS usually outperforms FSR, particularly in handling motion.
The development would leave Intel as the only GPU maker without a video upscaling solution, but given their response in areas like super resolution and frame generation, it wouldn’t be surprising to see them develop a video upscaling solution based on XeSS, too. That would surely provide another selling point for the company’s latest CPUs, which include AI hardware features and integrated graphics that support machine learning-based upscaling.
The AMD Radeon Adrenalin driver update will also improve AVC, HEVC, and AV1 encoding on RDNA 3 GPUs.