Xiaolu Chu
Tesla (NASDAQ:TSLA) has been given a big boost in recent months which has been ignored by Wall Street. Another major player in the self-driving industry has faced a barrage of safety concerns and will likely scale down its ambitions. GM’s (GM) Cruise had received approval in August to start its round-the-clock robotaxi service in San Francisco. After a pedestrian accident and a few other issues, the company has decided to withdraw all 950 robotaxis nationwide. GM lost more than $3 billion on Cruise in 2023. Bloomberg has reported that Cruise is planning to resume robotaxi testing after suspension. However, after earlier layoffs and the exit of key executives, it is unlikely that Cruise will manage to regain its position in this segment. Tesla is facing cost pressures due to the rise of Chinese automakers and having a strong market share in autonomous driving should help the company improve margins and create differentiation. Mercedes and Baidu are trying to build their own autonomous driving capabilities but they face issues very similar to GM.
On the other hand, Google’s (GOOG) Waymo has been very successful in launching its robotaxis and has continued to enjoy approval of regulators and public. This shows that like many other industries, the self-driving business is also likely to be cornered by a few big tech players. Currently, the main players are Tesla, Google’s Waymo and Amazon’s (AMZN) Zoox. Each of them has its advantages which will allow them to build and retain a significant market share in the self-driving industry.
If the current expansion plans of Tesla are successful, the company will have over 100 million vehicles on the road in a decade. Tesla’s ability to test its self-driving software gives it a lead over other competitors. The autonomous driving trend will have a big impact on other lucrative categories trucking industry as well as last-mile delivery of e-commerce business. Tesla will likely be the only automaker with a full-fledged self-driving capability which should give the company better pricing power and margins compared to other automakers.
Challenges faced by Cruise changes everything
The rapid growth of Cruise and the massive resources allocated by GM showed that companies other than the Big Tech players could also enter the self-driving industry. However, the recent issues with Cruise will reduce the incentives for other non-tech companies to enter the self-driving business. This shows the scale of investment required to build a foothold in this industry. No other company or startup has the resources to absorb these losses other than the big tech companies. In 2022, Ford (F) and Volkswagen-backed Argo shut down after losses ran into billions of dollars. Mercedes is also building its autonomous driving but it will also face the same issues faced by GM and Ford. Baidu in China recently got a reality check and had to change key executives.
Another major startup in this industry is Aurora Innovation which has recently started a driverless route between Dallas and Houston. The company has a market cap of $4 billion and has a team that earlier worked on Google’s self-driving business. However, the road to monetization is still quite long and this startup will find it difficult to sustain investment during this time. There are a few other startups working on this problem but we could see consolidation in the industry due to heavy investment requirements in the early stages.
Only three Big Tech players will survive
It has been more than a decade since the massive testing within self-driving industry started. This business has shown a lot of promise but it has been difficult to get the regulatory approval. Even a minor accident could derail billions of dollars of investment by a big player. Few companies would like to risk this level of resources. In my opinion, even Apple (AAPL) with its massive resources would not be able to successfully enter the self-driving industry as it requires significant time and resources in the early stages of software development and testing.
It is becoming clear that most of the self-driving business will likely be cornered by three Big Tech companies – Tesla, Google’s Waymo, and Amazon’s Zoox. Despite the challenges faced by Cruise, Google’s Waymo has continued to receive support from regulators and the reviews of its driverless taxi by public have also been positive.
Tesla also has a big advantage in this industry. The company can quickly upgrade any software defects instantly on its FSD system. This has allowed Tesla to rack up more than 500 million miles by Q3 2023.
Tesla Filings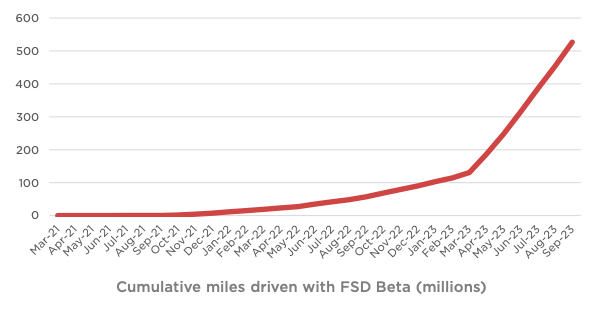
Figure: Cumulative miles driven with FSD Beta.
A higher production rate of Tesla cars in the future should further increase the pace at which autopilot miles are added. This gives Tesla a massive amount of data to experiment with new approaches within FSD. On the other hand, Waymo has managed to have less than 5 million miles with fully autonomous driving. Over the long run, most of the automakers would not be comfortable using Tesla’s FSD as it gives a big competitive advantage to Tesla. We could see Waymo gain greater acceptance among traditional automakers. Even ride-sharing leader Uber has announced a partnership with Waymo.
Tesla Filings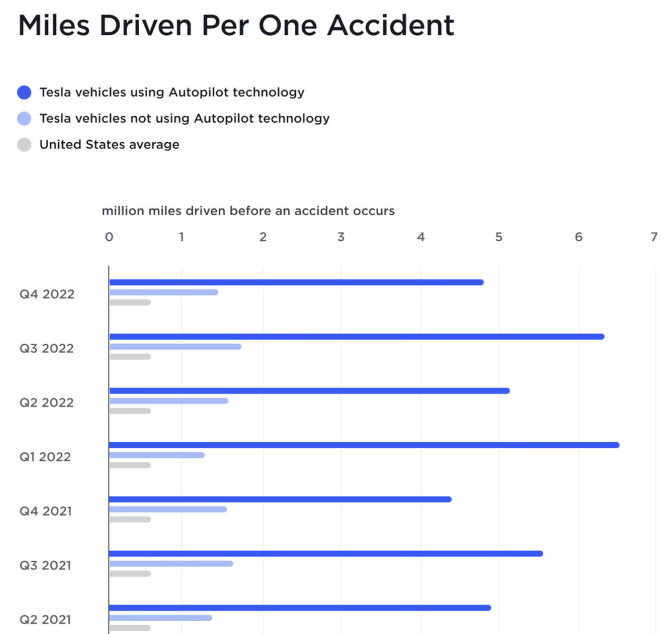
Figure: Tesla’s safety record as published by the company.
Tesla regularly publishes the safety record and it clearly shows a massive advantage of using Autopilot.
Better pricing power and increase in total addressable market
It can still take a number of quarters before we see self-driving cars achieve critical mass. However, this technology is likely to see an S-shaped curve similar to what we see in other cases. The inflection point for self-driving business could be sooner than current estimates. Robotrucks and robotaxis are the first targets for this technology. A significant fraction of the total cost in the transportation sector is due to the labor cost. Reduction in this cost should reduce the price of goods for end customers. Besides robotrucks and robotaxis, we should also see a massive uptick in the use of autonomous technology within e-commerce for last-mile delivery. This will reduce the fulfillment cost for packages which should improve the overall demand within e-commerce.
There are various estimates about the future addressable market for self-driving business. McKinsey & Company recently published its own estimates which claim that these systems could create $300 billion to $400 billion in revenue by 2035.
McKinsey & Company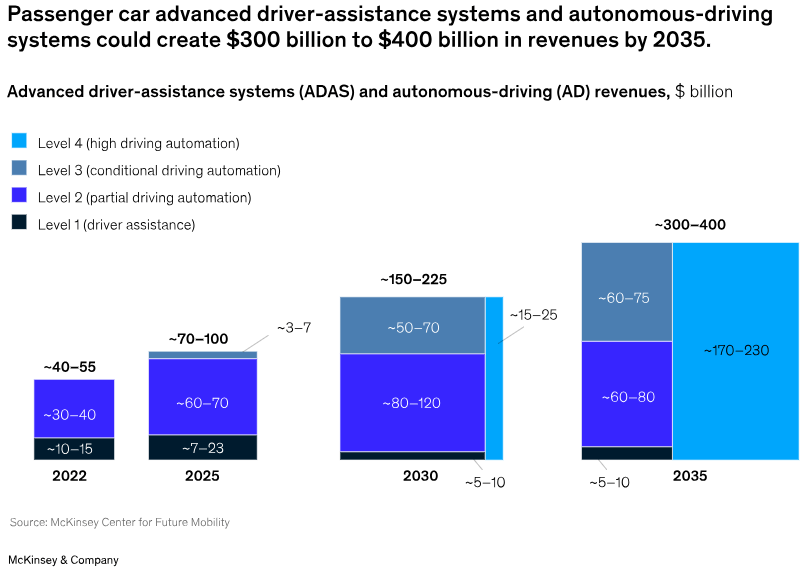
Figure: Autonomous driving revenue in the next few years.
It is also important to gauge the possible business model and profitability in this industry. Warren Buffett had earlier given the example of the airline industry many times saying that a massive revenue growth in an industry does not necessarily equate to a good business or an investment.
One of the core reasons why self-driving businesses are showing promise after the debacle of Cruise is that there will likely be very few additional competitors who would be willing to build their own self-driving business from scratch. Within the airline industry, new competitors can enter the business leasing a couple of airplanes with an initial investment of a few million dollars. However, the self-driving business has shown that the investment needed to map different locations along with rigorous safety testing can easily run into billions of dollars with no guarantee that a company will reach the monetization stage. There are only a couple of companies that can risk this kind of investment.
This factor gives a significant bullish tailwind to Tesla’s investment in self-driving. If the future market is going to be divided among the top 3 big players with Tesla being one of them, then the long-term profitability of this segment could be more resilient than forecasted.
Impact on Tesla stock
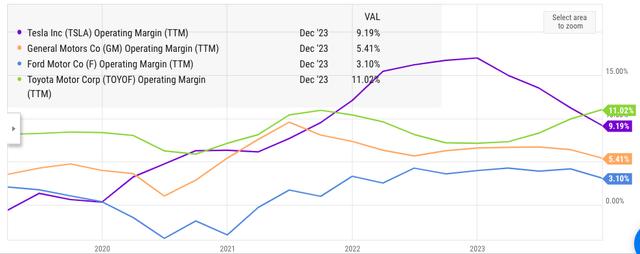
The future trajectory of Tesla stock will depend a lot on the services the company can offer to the customers. Self-driving is a key part of Tesla’s services and the monetization rate for this business will increase significantly as more regulatory approvals are given. Tesla will likely offer its own robotaxis and robotrucks after it develops customized products for these markets. The auto industry is a low-margin business and Tesla needs to show a high-margin service that can alleviate some of the cost pressures it is facing in production.
Figure: Tesla’s operating margin has fallen in the recent quarters.
FSD could do for Tesla what AWS did for Amazon. Without AWS, Amazon would not have been able to ramp up investment in logistics and invest in new growth segments.
The business model of self-driving industry is not clear but Tesla will gain product differentiation by having its own autonomous driving capacity. None of the other automakers would be able to boast of it besides those who license the technology from Google or Amazon. The failure of GM’s Cruise and earlier Ford’s Argo have shown the difficulty in launching a successful self-driving capacity. Tesla’s monetization of its FSD service could help the company generate higher margin service in its battle with traditional automakers.
Investor takeaway
We are seeing significant consolidation within the self-driving business. The recent failure of Cruise despite the strong backing of GM and investment of billions of dollars shows that the barrier to entry in this industry is very high. It is highly likely that only three main tech firms will corner a majority of market share in self-driving industry. They are Tesla, Google’s Waymo, and Amazon’s Zoox.
Tesla will gain a big product differentiation advantage over other traditional carmakers due to its FSD technology. Better monetization of this service is likely to happen in the next few quarters which will also give access to high-margin service revenue to Tesla. This should improve the operating margin of the company and effectively compete in the cost-cutting environment seen within the auto industry in recent quarters.