When you board a United Airlines plane, the gate agents, flight attendants and others involved in making sure your plane leaves on time are in a chatroom coordinating a lot of the work that you, as a passenger, will hopefully never notice. Is there still space for carry-on bags? Did the caterer bring the missing orange juice? Is there a way to seat a family together?
When a flight is delayed, a message with an explanation will arrive by text and in the United app. Most of the time, that message is generated by AI. Meanwhile, in offices around the world, dispatchers are looking at this real-time data to ensure that the crew can still legally fly the plane without running afoul with FAA regulations. And only a few weeks ago, United turned on its AI customer service chatbot.
Jason Birnbaum, who became United’s CIO in 2022, manages a team of over 1,500 employees and about 2,000 contractors who are responsible for all of the tech that makes this happen.
“What I love about our business is also what you hate about the business,” he told me in a recent interview. “I was at GE for many years in the appliance business; we could go down for a day, I don’t think anyone would notice. They’d be: ‘All right, the dishwashers aren’t rolling off the line.’ But it wasn’t newsworthy. Now if something happens, even for 15 minutes, not only is it all over social media but the news trucks head out to the airport.”
Before joining United, Birnbaum spent 16 years at GE, moving up the ladder from technology manager to becoming the CIO of GE Consumer and Industrial, based in Budapest. In 2009, he became the CI of GE Healthcare Global Supply Chain. He joined United in 2015 as its SVP of Digital Technology, where he was responsible for launching projects like ConnectionSaver, one of United’s first AI/ML-based services that will proactively hold flights when fliers have tight connections (and that saved me from spending 12 hours at SFO last week).
I wanted to talk to Birnbaum about how he — and other CIOs at global enterprises — are thinking about the use of AI. That’s one area of innovation the airline is looking at. But before we could talk about AI, United is also still in the process of moving services into the cloud. If there’s one trend in cloud computing right now, it’s that everybody is trying to optimize their cloud infrastructure and spend less.
“I’m starting to see these companies and startups that are, ‘How do you optimize your cloud, and how do you manage your cloud?’ There’s a lot of people focused on questions like, ‘You’ve got a lot of data, can I store it better for you?’ Or, ‘You’ve got a lot of new applications; can I help you monitor them better?’ Because all the tools you used to have don’t work anymore,” he said. Maybe the age of digital transformation is over, he said, and we’re now in the age of cloud optimization.
United itself has bet heavily on the cloud, specifically AWS as its preferred cloud provider. Unsurprisingly, United, too, is looking at how the company can optimize its cloud usage, from both a cost and reliability perspective. Like for so many companies that are going through this process, that also means looking at developer productivity and adding automation and DevOps practices into the mix. “We’re there. We have an established presence [in the cloud], but now we’re kind of in the market to try to continue to optimize as well,” Birnbaum said.
But that also comes back to reliability. Like all airlines, United still operates a lot of legacy systems — and they still work. “Frankly, we are extra careful as we move through this journey, to make sure we don’t disrupt the operation or create self-inflicted wounds,” he said.
United has already moved and turned off a lot of legacy systems, and that process is ongoing. Later this year, for example, the company will turn off a large Unisys-based system. But Birnbaum also thinks that United will continue to have on-prem systems. “I just want to be in the best places for the applications and for the user experience,” he said, whether that’s for performance, privacy or security reasons.
The one thing the company is not trying to build, though, is some kind of overarching United Platform that will run all of its systems. But there’s too much complexity in the day-to-day airline operations to do that, Birnbaum said. Some platforms manage reservations, ticketing and bag tracking, for example, while others handle crew assignments.
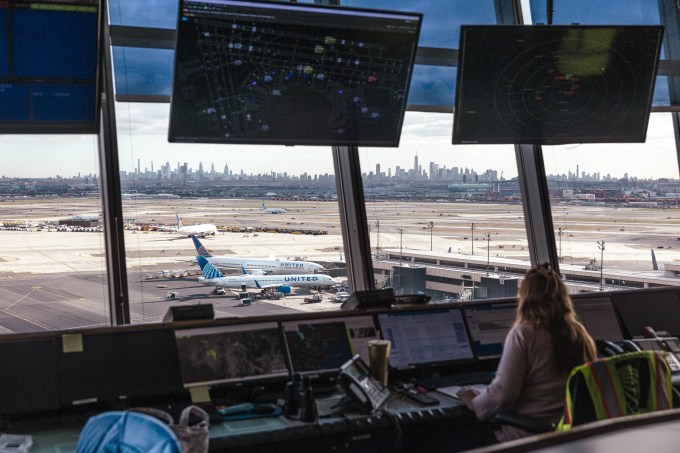

A worker in the United Airlines Station Operation Center at Newark Liberty International Airport in Newark, New Jersey. Image Credits: Angus Mordant/Bloomberg via Getty Images
When something goes wrong, those systems have to work together and in near real time. That’s also why United is betting on one cloud provider. “I don’t imagine we’ll have one platform,” Birnbaum said. “I think we’re going to get really good at connecting things and getting applications to talk to each other.”
In practice, that means that today it’s possible for the team to see when the caterer got off the plane and who has checked in for the flight, for example. And the ground teams and flight attendant crews can see all of that through their internal chat app, too.
Every flight has an AI story
While all of this work is still going on, United is also looking at how it can best leverage AI.
One story I regularly hear about AI/ML in large enterprises is that ChatGPT didn’t necessarily change how the technologists thought about it, but that it suddenly became a boardroom discussion. That also holds true for United.
“We had a pretty mature AI practice,” Birnbaum said when I asked him when he realized that generative AI was something the team had to pay attention to. “We built a lot of capabilities to manage models, to do tuning and all that. So the good news for us was that we had already made a pretty big investment in this capability. What changed [when ChatGPT arrived] was not that we had to take it seriously. It was who was asking about it: When the CEO and the board suddenly are saying: ‘Hey, I need to know more about this.’”
United is quite bullish on AI, Birnbaum said. “I think the travel industry has so many different examples of where AI can be used both for the customer and for the employees.” One of those is United’s “Every flight has a story.”
Not that long ago, it was rather typical to get a notification when a flight was delayed, but no further information about it. Maybe the incoming flight was delayed. Maybe there was a maintenance issue. A few years ago, United started using agents to write short notices that explained the delay and sent those out through its app and as text messages. Now, pulling in data from its chat app and other sources, the vast majority of these messages are written by AI.
Similarly, United is looking at also using generative AI to summarize flight information for its operations teams, so they can get a quick overview of what’s happening.
Just a few weeks ago, United fully moved its chat system on United.com to an AI agent, too. In my own tests, that system still felt quite limited, but it’s only a start, Birnbaum said.
Famously, Air Canada once used an AI bot that sometimes gave wrong answers, but Birnbaum said he wasn’t too worried about that. From a technical perspective, the bot draws upon United’s knowledge base, which should keep hallucinations under control. “But to me [the Air Canada incident] wasn’t a technology failure, that was a customer service failure because — and I won’t comment too much — but I would say that, today, our human agents give wrong answers, too. We just have to deal with that and move on. I think we’re very prepared for that situation,” Birnbaum said.
Later this year, United also plans to launch a tool that is currently called “Get Me Close.” Often, when there’s a delay, customers are willing to change their plans to switch to a nearby airport. I once had United switch me to a flight to Amsterdam when my flight to Berlin got canceled (not that close, but close enough to get a train and still moderate a keynote session the next morning).
“While our mobile tools are great — and they are excellent — when people go talk to humans, the interactions are usually more about building optionality. Meaning you’re going to say, ‘Well, your flight’s delayed’ and then someone might say, ‘Well could you get me to Philadelphia instead of New York? Could you get me close? We believe that interaction is a great use case for AI.”
AI for pilots?
After creating the system that automatically writes the delay “stories” in the app, Birnbaum’s team is now thinking about where it can use the same generative AI technology. One area: those short briefings pilots usually give before takeoff.
“A pilot actually came up to me and said, ‘One of the things that some pilots are great at is getting on that speaker and saying, “Hey, welcome, everybody going to Las Vegas, blah blah.”’ And he said, ‘Some pilots are introverted; could you have an AI engine that helps me generate an announcement on the plane about where I’m going so that I could give a really good announcement about what’s happening?’ And I thought that was a great use case.”
As it turns out, one of the main drivers of customer satisfaction for airlines is actually pilot interaction. A few years ago, United started focusing on its Net Promotor score and asked pilots to make announcements about delays while standing at the front of the cabin, for example. It makes sense for the airline to look at how it can improve upon such a crucial interaction — while hopefully still allowing for pilots to go off-script, too.
Another area where generative AI may help pilots is in summarizing complex technical documents. But as Birnbaum rightly noted, everything that involves the pilot flying the plane is heavily structured and regulated, so it’ll be a while before the airline will launch anything there.